Let's install Docker.
But first, you need to update the OS packages.apt update
Install the necessary packages and add a new repository:
apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg-agent software-properties-common curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt key add - add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable"[/code] Update the packages with the new repository:
apt update
Now let's install Docker itself.
apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
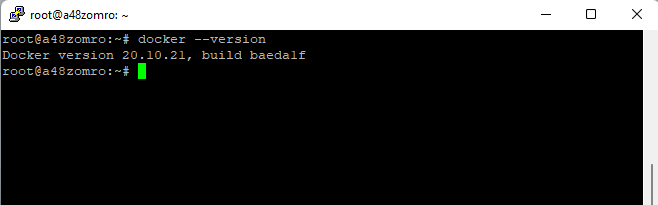
Let's check the version:
docker --version
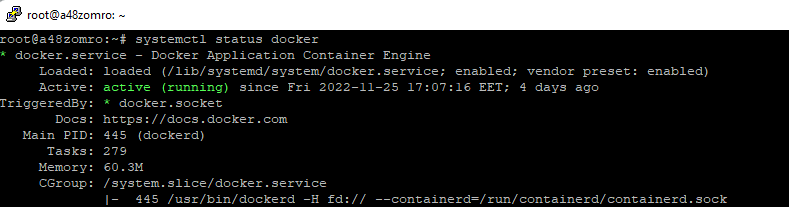
 Let's check the status:
Let's check the status:systemctl status docker
If it does not start, then run:
systemctl start docker
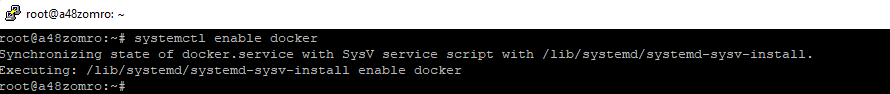
And add to autorun.
systemctl enable docker
Install Docker Compose
curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.25.5/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin /docker-compose
Set permissions to launch.
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
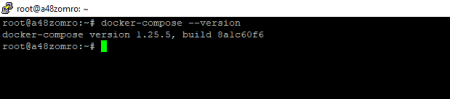
Check how Docker-Compose was installed:
docker-compose --version
Let's create a *.yaml file for Docker-Compose.
To navigate in the future in what we have installed, let's create a separate folder for this project in the /home directory and go to it.
mkdir /home/postgres && cd /home/postgres
You can also use a different directory to host this and other projects.
Let's use the repository to create the docker-compose.yaml file at https://hub.docker.com/_/postgres
Create a docker-compose.yaml or docker-compose.yml file,
vim docker-compose.yaml
And add the following code to it:
version: '3.8'
services:
db_postgres:
image:postgres
container_name: postgres
restart: always
environment:
POSTGRES_USER:root
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: root
POSTGRES_DB: test_db
ports:
- "54320:5432"
volumes:
- local_pgdаta:/var/lib/postgresql/data
pgadmin4:
container_name: pgadmin4
image:dpage/pgadmin4
restart: always
environment:
PGADMIN_DEFAULT_EMAIL: admin@a48zomro.ml
PGADMIN_DEFAULT_PASSWORD: root
ports:
- "5050:80"
volumes:
- pgadmin-dаta:/var/lib/pgadmin
volumes:
local_pgdаta:
pgadmin-dаta:Where:
container_name: name of your container;
POSTGRES_USER: The user for the database being created;
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: password for the user we are creating;
POSTGRES_DB: database name;
PGADMIN_DEFAULT_EMAIL: mail/user for authorization in pgadmin;
PGADMIN_DEFAULT_PASSWORD: password for the pgadmin user;
5050:80: the port on which pgadmin is running.
Run our script (for this you need to be in the directory where our file was created. In this case, it is /home/postgres):
docker-compose up -d
We check:
docker-compose ps
or
docker ps
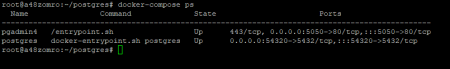
Now you can use the container IP with port 54320, or the name of the postgres container with port 54320 (IP:54320 or postgres:54320) to connect the database.
To view the logs, use the command
docker logs -f postgres
To configure pgadmin - open a browser and go to - http://YOUR_IP_SERVER:5050/ . In the connection details for the hostname, specify the postgreSQL container name or the mail that was specified in PGADMIN_DEFAULT_EMAIL and the root password
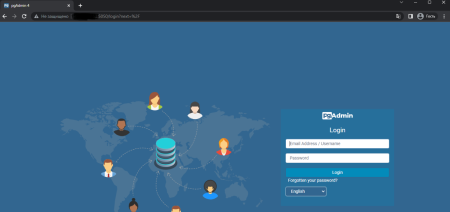
Now let's connect the postgreSQL database server to pgadmin4.
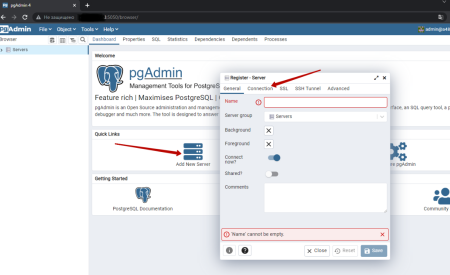
We enter the data indicated by docker-compose.yaml
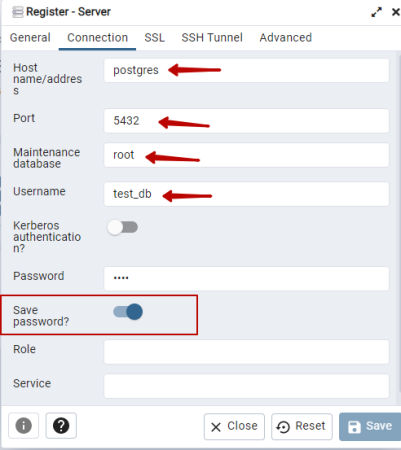
Now you can create postgreSQL databases in pgadmin4.

