Remote control of computers has become an important part of daily work for many IT professionals. However, with this comes certain security risks. One of these risks is remote desktop root-forwarding (RDP) attacks. In this article, we will look at how to protect a RDP connection from bruteforce using the IPBan tool.
As we know, a bruteforce attack is a cyberattack method where an attacker tries to guess a password using all possible combinations of characters until he finds the right one. In the case of RDP, the attacker can gain access to your computer if the username and password are matched.
What is IPBan and how does it work?
IPBan is free and open-source software designed to protect against bruteforce attacks on various services such as RDP, FTP, SQL and others. IPBan monitors failed login attempts and blocks IP addresses from which attacks are launched.
Installing IPBan
1. Download IPBan from the official website: https://github.com/DigitalRuby/IPBan/releases
2. Unzip the archive and move the IPBan folder to a convenient location on your computer.
3. Run the executable file IPBan.exe with administrator rights (right click and select "Run as administrator").
Configuring IPBan
1. Find the IPBan.config file in the IPBan folder and open it with Notepad or another text editor.
2. modify the parameters in the configuration file to suit your needs. The main parameters to change are:
- "banTime": the time for which an IP address will be blocked after a certain number of failed attempts. Set it according to your security requirements (e.g. "1.00:00:00" to block for 1 day).
"failedLoginAttemptsBeforeBan": the number of failed login attempts after which the IP address will be blocked. It is recommended to set this value not too low to avoid false positives.
"whitelist": a list of IP addresses that will never be blocked. Enter the IP addresses from which you always want to access RDP, such as your home or office IP address.
Save your changes and close the configuration file.
Launch IPBan.
Run IPBan.exe with administrative privileges (if you have not already done so).
If executed successfully, IPBan will run in the background and block IP addresses from which bruteforce attacks are launched.

Checking IPBan operation
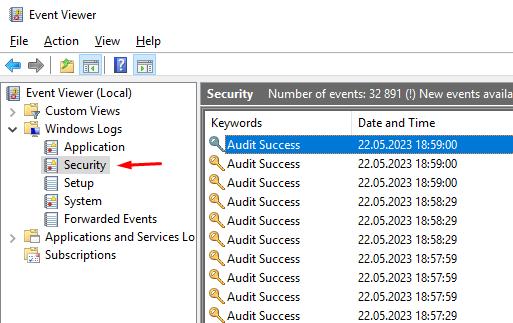
Open the Event Viewer in Windows and look for "Windows Logs".

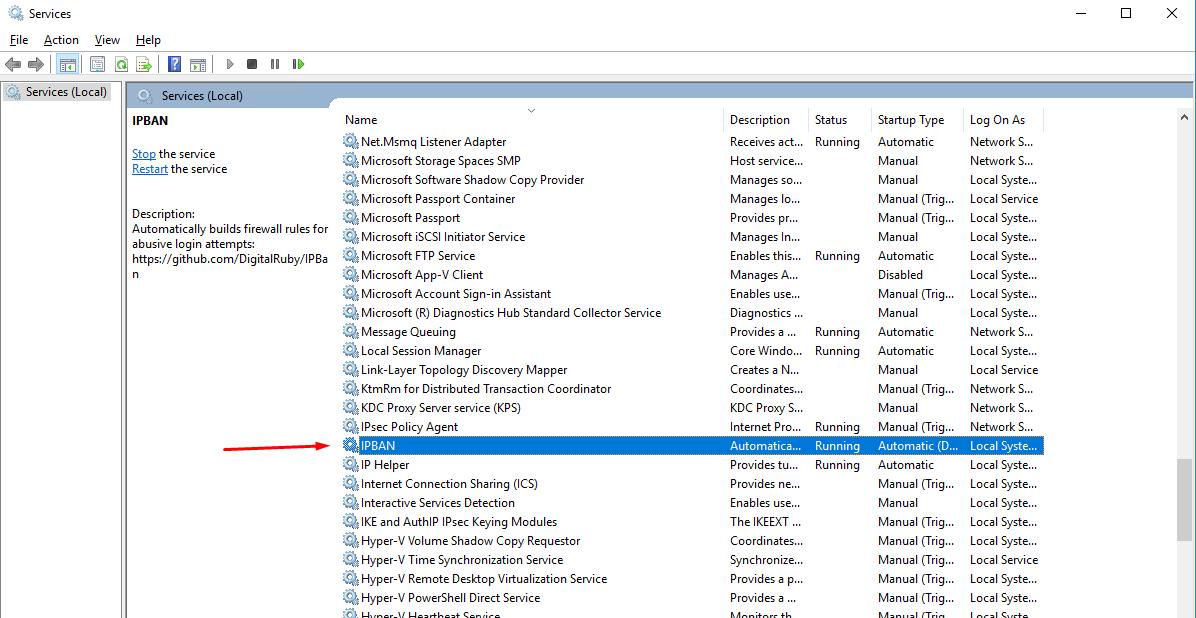
You can also see how the IPBAN service works by running the command: services.msc
Open the "Security" section to see records of login attempts and IP blocking.
Verify that IPBan is successfully blocking attacking IPs.
Conclusion
Using IPBan is an effective way to protect your RDP connection from bruteforce attacks. However, in addition to IPBan, other security measures are recommended, such as using complex passwords, limiting RDP access to only trusted IP addresses, and regularly updating your operating system and anti-virus software.
By following the instructions in this article, even novice users can effectively protect their RDP connections from bruteforce attacks, increasing the security of their computer systems.
Translated with www.DeepL.com/Translator (free version)

